Setting up an emulation with Simu5G and OpenNESS¶
This page describes how to setup an emulation scenario where a (real) client application communicates with a (real) Edge Application running in the MEC environment provided by Openness, through a 5G network emulated by Simu5G.
The integration of Simu5G and Openness has been described in our PIMRC 2020 paper:
G. Nardini, G. Stea, A. Virdis, D. Sabella, P. Thakkar, “Using Simu5G as a Realtime Network Emulator to Test MEC Apps in an End-To-End 5G Testbed”, PiMRC 2020, London, UK, 1-3 September 2020
Emulation scenario¶
We refer to a simple video streaming Edge App, which implements one server instance of the well-known VLC software (note that the Edge App can be replaced with any other application). The client application (running on the UE side) is the commercial version of the VLC media player. Two scenarios can be deployed:
Client application, i.e. the VLC player app, running on the same host where Simu5G runs (if the hardware allows it).
Client application, i.e. the VLC player appe, running on a different host from where Simu5G runs.
You can refer to the configuration files present in the emulation/extclientserver folder as a starting point for the emulation.
OpenNESS installation and configuration¶
Please refer to the official OpenNESS documentation. In this guide, we refer to Openness v20.06.
Client application on the same host of Simu5G¶
In the following, we refer to the architecture depicted in the figure:
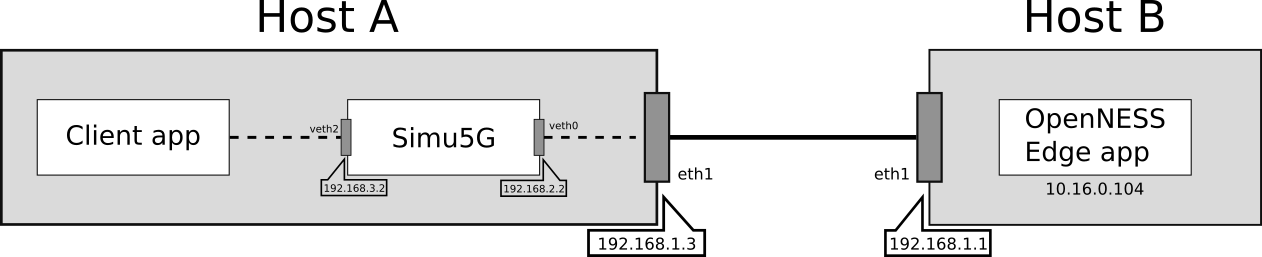
The main components of the above architecture are:
Host A, which acts as a client and requests a service from the OpenNESS server and which also emulates the 5G network by running an instance of Simu5G in real-time mode;
Host B, which runs an instance of OpenNESS and acts as the video-streaming application server.
Host B runs a containeraized Edge App reachable at 10.16.0.104:8080 and the hosts interfaces and IP addresses are configured as shown in the figure.
Regarding the emulated network scenario, we refer to the “EmulatedNetwork” example, shown in the figure below.
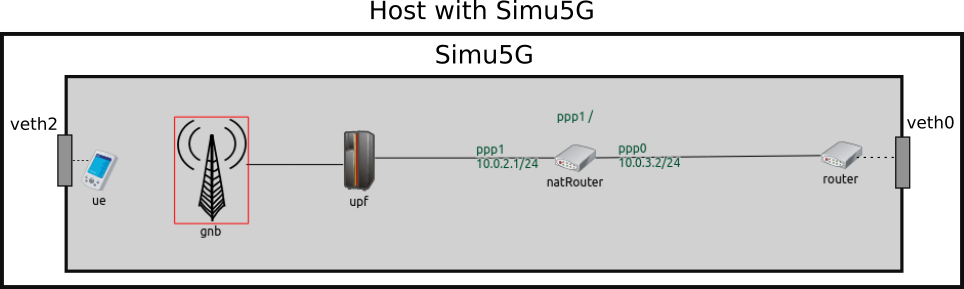
The router and the UE are endowed with an ExtLowerEthernetInterface module, which is capable to receive real packets received by a network interface card attached to it. The latter is virtual and is created as a veth device. This way, data packets coming to the veth attached to Simu5G are injected into the “ue” element of the running instance of it. From there, data are forwarded through the emulated NR network towards the router. When data packets reach the router, they are sent out to Edge App via a veth attached to it. Vice versa, packets coming from the Edge App are injected into the “router” element of the running instance of Simu5G and forwarded to the “ue”, which sends them out to the Client application.
The natRouter is used in order to run an emulation in which both the endpoints of a connection are real applications, so the client application needs to use the IP address of the NAT router within the simulation as destination address. Such NAT router element will perform Network Address Translation (NAT), according to the rules specified with the corresponding parameter in the INI file.
Setting the environment¶
In order to setup the above scenario, the following steps are required to configure the OS on Host A (the one running Simu5G).
Note
The following instructions refer to a host equipped with Linux Ubuntu 18.04 OS.
Configure the network¶
We need to configure the Host A’s OS so that it can reroute packets from the veth interface connected to Simu5G to the Host B
Enable IP forwarding on Host A, by running “sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf” from the terminal. Look for the ip_forward parameter and edit it as follows:
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1It could be possible that Host B machine cannot be accessed by the user, so the routing table cannot be modified in order to add the route for the natRouter (in Simu5G). For this reason, Host A performs NAT by changing the natRouter source address with the Host A interface address connected to Host B.
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -d 10.16.0.104 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE sudo iptables-save sudo iptables -LAdd IP route for packets destined to the container running the Edge App on Host B:
sudo route add -net 10.16.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1 dev eth1
Note
routes to inject packet into Simu5G, i.e the veth interfaces management, are automatically added by the run_wSocket.sh script present in the emulation/extclientserver folder.
Configure the simulation¶
The emulation/extclientserver folder includes an exemplary omnetpp.ini file. You can use it as a starting point for your own configuration.
In the omnetpp.ini file, set the UE’s ‘extHostAddress’ parameter to the IP address of the veth2 interface
*.ue.extHostAddress = "192.168.3.2"Configure the routing tables of all the network devices in the simulated network. To do so, edit the .mrt files included in the folder ‘routing’. Edit them so as to enable a path from the router to the UE. In the omnetpp.ini file, set the ‘routingTable.routingFiles’ parameters to the path of the .mrt files.
In the omnetpp.ini file, set the ‘device’ parameters for both the router and the UE. It is the name of the virtual interfaces which you want to capture the packets
*.ue.eth[0].device = "veth2"*.router.eth[0].device = "veth0"Configure NAT rules:
The destination address known by the client application is 10.0.2.1, while the real Edge App address is 10.16.0.104.
The destination address known by the Edge App is 10.0.3.2, while the real client application address is 192.168.3.2 (i.e. the address of the veth2 interface).
*.router.ipv4.natTable.config = xml(" <config> <entry type='prerouting' packetDataFilter='*Ipv4Header and destAddress=~10.0.2.1' srcAddress='10.0.3.2' destAddress='10.16.0.104'> <entry type='prerouting' packetDataFilter='*Ipv4Header and destAddress=~10.0.3.2' srcAddress='10.0.2.1' destAddress='192.168.3.2'> </config> ")
Run the scenario¶
Note
the INET framework must be compiled with the Network Emulation Support feature enabled! To enable it (if not): open the OMNeT++ IDE > select the inet projet > Projet tab > select Project Features > Network Emulation Support
In your terminal, navigate to the “simulations/emulation” folder
Run the simulation with root privileges, by typing:
sudo ./run_wSocket.shThis is needed for running the simulation in real time mode. As already mentioned, such script also contains the creation and the management of the veth interfaces.
Open VLC client > Ctrl-N > enter the network URL as: http://10.0.2.1:8080
Enjoy the movie coming from a 5G mobile network!
Client application on a different host from where Simu5G runs¶
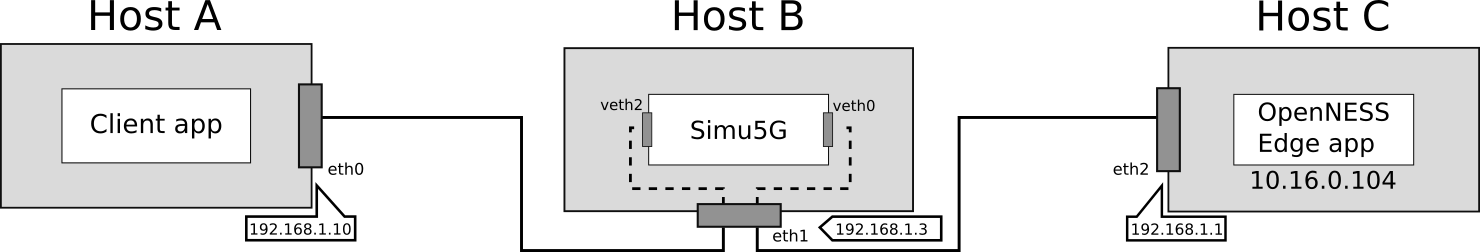
The main components of the above architecture are:
Host A, which acts as a client and requests a service from the OpenNESS server
Host B, which emulates the 5G network by running an instance of Simu5G in real-time mode
Host C, which runs an instance of OpenNESS and acts as the video-streaming application server
Host C runs a containeraized Edge App reachable at 10.16.0.104:8080 and the hosts interfaces and IP addresses are configured as shown in the figure.
Regarding the emulated network scenario, we refer to the “EmulatedNetwork” example, shown in the figure below.

The router and the UE are endowed with an ExtLowerInterface module, which is capable to receive real packets received by a network interface card attached to it. The latter is virtual and is created as a veth device. This way, data packets coming to the veth attached to Simu5G are injected into the “ue” element of the running instance of. From there, data are forwarded through the emulated NR network towards the router. When data packets reach the router, they are sent out to Edge App via a veth attached to it. Vice versa, packets coming from the Edge App are injected into the “router” element of the running instance of Simu5G and forwarded to the “ue”, which sends them out to the Client application.
The natRouter is used in order to run an emulation in which both the endpoints of a connection are real applications, so the client application needs to use the IP address of the NAT router within the simulation as destination address. Such NAT router element will perform Network Address Translation (NAT), according to the rules specified with the corresponding parameter in the INI file.
Setting the environment¶
In order to setup the above scenario, the following steps are required to configure the OS on Host B (the one running Simu5G).
Note
The following instructions refer to a host equipped with Linux Ubuntu 18.04 OS.
Configure the network¶
We need to configure the Host B OS so that it can reroute packets from the veth interfaces connected to Simu5G to Host A and Host C.
Enable IP forwarding on Host B, by running “sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf” from the terminal. Look for the ip_forward parameter and edit it as follows:
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1It could be possible that Host C machine cannot be accessed by the user, so the routing table cannot be modified in order to add the route for the natRouter (in Simu5G). For this reason, Host B performs NAT by changing the natRouter source address with the Host B interface address connected to Host C.
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -d 10.16.0.104 -o eth1 -j MASQUERADE sudo iptables-save sudo iptables -LAdd IP route for packets destined to the container running the Edge App on Host C:
sudo route add -net 10.16.0.0/24 via 192.168.1.1 dev eth1
On Host A
Add IP route for packets destined to the natRouter running in Simu5G:
sudo route add -net 10.0.2.0/24 via 192.168.1.3 dev eth0
Note
routes to inject packet into Simu5G, i.e the veth interfaces management, are automatically added by the run_wSocket.sh script present in the emulation/extclientserver folder.
Configure the simulation¶
The emulation/extclientserver folder includes an exemplary omnetpp.ini file. You can use it as a starting point for your own configuration.
In the omnetpp.ini file, set the UE’s ‘extHostAddress’ parameter to the IP address of the Hosta A eth0 interface
*.ue.extHostAddress = "192.168.1.10"Configure the routing tables of all the network devices in the simulated network. To do so, edit the .mrt files included in the folder ‘routing’. Edit them so as to enable a path from the router to the UE. In the omnetpp.ini file, set the ‘routingTable.routingFiles’ parameters to the path of the .mrt files.
In the omnetpp.ini file, set the ‘device’ parameters for both the router and the UE. It is the name of the veth interfaces which you want to capture the packets
*.ue.eth[0].device = "veth2"*.router.eth[0].device = "veth0"Configure NAT rules:
The destination address known by the client application is 10.0.2.1, while the real Edge App address is 10.16.0.104.
The destination address known by the Edge App is 10.0.3.2, while the real client application address is 192.168.1.10.
*.router.ipv4.natTable.config = xml(" <config> <entry type='prerouting' packetDataFilter='*Ipv4Header and destAddress=~10.0.2.1' srcAddress='10.0.3.2' destAddress='10.16.0.104'> <entry type='prerouting' packetDataFilter='*Ipv4Header and destAddress=~10.0.3.2' srcAddress='10.0.2.1' destAddress='192.168.1.10'> </config> ")
Run the scenario¶
Note
the INET framework must be compiled with the Network Emulation Support feature enabled! To enable it (if not): open the OMNeT++ IDE > select the inet projet > Projet tab > select Project Features > Network Emulation Support > recompile the inet project
In your terminal, navigate to the “simulations/emulation” folder
Run the simulation with root privileges, by typing:
sudo ./run_wSocket.shThis is needed for running the simulation in real time mode. As already mentioned, such script also contains the creation and the management of the veth interfaces.
Open VLC client on Host A > Ctrl-N > enter the network URL as: http://10.0.2.1:8080
Enjoy the movie coming from a 5G mobile network!